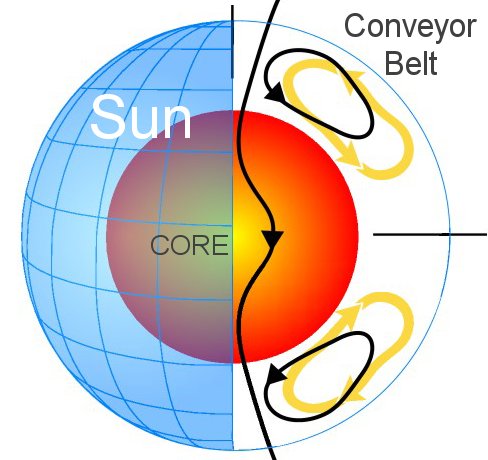
I browsed through my copy of QST magazine yesterday. QST is the publication of the American Radio Relay League, an amateur radio (ham radio) organization. In it, I read an interesting scientific hypothesis explaining the dearth of sunspots we have seen over the past several years. The theory holds that plasma currents deep inside the sun may have interfered with the formation of sunspots and prolonged the solar minimum.
Later in the article, there is mention of a secondary consequence of the minimum in that “space junk” can remain in low Earth orbit due to the upper atmosphere collapsing. You can read this very interesting article at this link.
NASA-sponsored research has resulted in the first computer model that explains the recent period of decreased solar activity during the sun’s 11-year cycle.
This recent solar minimum, a period characterized by a lower frequency of sunspots and solar storms, was the deepest observed in almost 100 years. The solar minimum has repercussions on the safety of space travel and the amount of orbital debris our planet accumulates.
. . .
During this deep solar minimum, the sun’s magnetic field weakened, allowing cosmic rays to penetrate the solar system in record numbers, making space a more dangerous place to travel. At the same time, the decrease in ultraviolet radiation caused Earth’s upper atmosphere to cool and collapse.
As a consequence space debris stopped decaying and started accumulating in Earth orbit due to decreased atmospheric drag. These effects demonstrate the importance of understanding the entire solar cycle, during both minimum and maximum.
Emphasis added.



 Maybe not.
Maybe not.